Recombinant Human NGAL Protein
Type: His-6 tag at N-terminal
Product Number:21231215
Size: 0.1 mg/1 mg/5 mg
Synonyms: 24p3, MSFI, LCN2
Accession Number: ACD02429
Source: E coli BL21 strain
Biology Activity: specific to human NGAL antibody.
Molecular Weight: 23.8 kDa by reducing SDS-PAGE.
Formulation: 1x PBS with 0.05% Tween 20, pH 7.4.
Purity: >97% as analyzed by reducing SDS-PAGE.
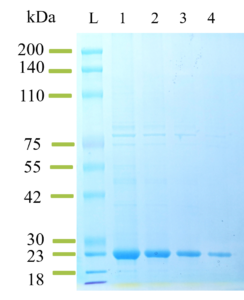
Fig0126241 SDS-PAGE of NGAL Proteins
L, AmeriDx® Protein Ladder; 1-4, 10 ug, 5 ug, 2.5 ug and 1 ug of recombinant NGAL/LCN2 from E coli. Lot# A0123241.
Endotoxin Level: < 0.1 EU/μg, determined by gel clot method.
Product Description
Human NGAL (Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin) is encoded by the LCN2 gene. NGAL is involved in innate immunity by sequestrating iron that in turn limits bacterial growth. It is expressed in neutrophils and in low levels in the kidney, prostate, and epithelia of the respiratory and alimentary tracts. NGAL is used as a biomarker of kidney injury1,2, and other cardiovascular disease and cancer3,4. NGAL can be measured in different samples, such as plasma, serum, urine3, or tissue homogenates, using ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) kits.
Components
Purified proteins in lyophilized format.
Protein Sequence
>ACD02429.1
MVPLGLLWLGLALLGALHAQAQDSTSDLIPAPPLSKVPLQQNFQDNQFQGKWYVVGLAGNAILREDKDPQKMYATIYELKEDKSYNVTSVLFRKKKCDYWIRTFVPGCQPGEFTLGNIKSYPGLTSYLVRVVSTNYNQHAMVFFKKVSQNREYFKITLYGRTKELTSELKENFIRFSKSLGLPENHIVFPVPIDQCIDG
Preparation Instructions
This protein is soluble in 1x PBS.
Storage/Stability
Recombinant NGAL protein remains stable up to 3 years at or below -20oC from date of receipt.
Avoid freeze-thaw cycles.
Precautions and Disclaimer
For Research Use Only. Not for drug, household, or other uses.
References
- Bagshaw, S. M., & Bellomo, R. (2007). The utility of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a marker of acute kidney injury (AKI) in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Medicine, 33(2), 208-210.
- Haase, M., Bellomo, R., Devarajan, P., Schlattmann, P., Haase-Fielitz, A., & NGAL Meta-analysis Investigator Group. (2011). Accuracy of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) in diagnosis and prognosis in acute kidney injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 58(6), 899-910.
- Haase, M., Haase-Fielitz, A., Bellomo, R., Devarajan, P., Story, D., Matalanis, G., … & Dragun, D. (2009). Sodium bicarbonate to prevent increases in serum creatinine after cardiac surgery: a pilot double-blind, randomized controlled trial. Critical Care Medicine, 37(1), 39-47.
- Mishra, J., Dent, C., Tarabishi, R., Mitsnefes, M. M., Ma, Q., Kelly, C., … & Devarajan, P. (2005). Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) as a biomarker for acute renal injury after cardiac surgery. The Lancet, 365(9466), 1231-1238.
